Incentive Pay 101: A Guide to Implementation, Benefits and More
Incentive pay is a powerful tool to drive employee motivation and performance. Learn how to structure an effective incentive pay program that aligns with business goals and rewards success.
On this page
Motivation is a catalyst for better performance. In an organization, incentives motivate employees toward efficient performance. The sales team has a huge task of generating more prospects. Incentive pay is a big boost for them in this process. We will discuss incentive pay and how you can design a systematic pay program.
What is incentive pay?
Incentive pay is the additional, variable benefit sales team members earn apart from their regular salary. This is calculated in relation to their performance and contribution to business goals.
These incentives may be monetary or non-monetary. They may be distributed to all without any fixed criteria or to a specific member for meeting certain goals. If implemented well, a business may notice that:
- The employees feel motivated when offered incentives in addition to their regular salary. They get more involved with their work and effectively contribute to the business goals.
- An uninterested employee may take frequent leaves. This affects the company and also increases its cost. Incentives reduce absenteeism by improving the morale of the staff.
- It encourages high performance and exceptional customer service within the sales team.
- It also establishes quality benchmarks within the sales reps to foster a productive and collaborative company culture.
But there are pros and cons to incentive pay which a company should know to design the aptly structured incentive pay plan.
Pros and cons of incentive pay:
Following are the pros and cons of incentive pay:
Pros:
Incentive pay offers several benefits. It boosts employee productivity and motivation. Morale improves when goals align with company objectives.
- Improves employee productivity: Rewards encourage harder work toward specific goals. Incentive pay motivates even those not meeting targets.
- Increases employee retention: Showing appreciation builds loyalty. Valued employees stay longer. This reduces turnover costs and boosts stability.
- Enhances organizational climate: Incentive pay improves workplace perception. It attracts talent by motivating employees. Team incentives promote collaboration and break down barriers.
Cons:
Incentive pay also presents some downsides. Focus can shift from performance to rewards. This might reduce cooperation and quality.
- Only provides a short-term benefit: Motivation might not last. Tunnel vision can develop, hurting creativity and increasing stress.
- Affects employee ethical behavior: Unethical shortcuts may occur to meet goals. Employees may feel pressured to act dishonestly for bonuses.
- Unhealthy work environment: Competition can foster theft and cheating. Some employees may feel undervalued. This can cause tension and conflict.
What are the differences between incentive pay, merit pay, and bonuses?
These are all ways to reward employees. However, they work differently. Incentive pay is for achieving specific goals. Merit pays increases base salary based on performance. Bonuses are one-time rewards.
Feature | Incentive Pay | Merit Pay | Bonus |
What it is | Pay for specific achievements. | Increase base pay for performance. | One-time reward. |
Frequency | Varies; project or goal based. | Typically, annual. | Varies; can be regular or irregular. |
Impact | Variable pay. | Permanent increase to base pay. | One-time payment. |
Based on | Specific, measurable goals. | Overall performance. | Individual or company performance. |
Example | Sales commission. | Annual raise based on review. | Holiday bonus. |
Incentive pay: Casual vs. structured
Incentives are of two types: casual and structured. Casual incentives are small gifts. Vouchers are an example. They show appreciation for hard work. They are not scheduled.
Structured incentives are planned. They are monitored. They aim to achieve targets. Sales growth is an example. Year-end bonuses are common.
Feature | Casual Incentives | Structured Incentives |
Nature | Small gifts, tokens | Planned and monitored programs |
Purpose | Show appreciation | Achieve specific targets |
Schedule | Unscheduled | Scheduled |
Examples | Vouchers | Year-end bonuses |
Target Metrics | No Predetermined Metrics | Sales, Customer Satisfaction, Production efficiency |
17 Types of incentive pay you can implement in your plan
Incentives can be monetary or non-monetary. Here is a list of incentives offered to the employees to improve their morale.
8 Monetary incentives
Incentives, where the reward is in the form of money, are called monetary incentives. Let us take a look at some of them.
- Bonus: A yearly bonus is issued in many organizations. This is not linked to the performance but is given to all alike. This is over and above the regular monthly salary given to motivate employees.
- Profit sharing: Employees are given a bonus as a percentage of the total profits earned by the company. This entirely depends on the profits earned in a year. This annual payout depends on the company’s overall performance and not on any individual target achievement. If the profits are higher, the bonus also increases.
- Gain sharing: Gain sharing has an underlying condition. Here, the company expects the employees to achieve certain targets or fixes a performance criterion. When the same is achieved, the employees are paid a bonus. This should not be confused with profit sharing. The employees are paid bonuses relative to their performance only.
- Annual incentives: This annual payment is matched as a percentage of the employee’s salary. This lump sum is paid when the employees reach the targets set for them. It may or may not be paid in any particular year.
- Spot rewards: Rewarding on the spot is a strategy that goes well with the employees. Instant recognition without waiting for the year-end or completion of appraisal is a motivator for the employees. This can be monetary or non-monetary. As and when an employee achieves something special, he is recognized through spot rewards.
- Project bonus: This bonus category is given to a set of employees who work on a particular project. The project manager assesses each team member's contribution and determines the bonus on the successful completion of the project. The percentage of the bonus is fixed at the start of the project.
- Merit-based bonus: As the name indicates, this bonus is related to the performance of the employees. Every year, an appraisal is conducted, during which the team leader assesses the employee's contribution in relation to the goals and suggests areas for improvement. A fixed percentage of salary is paid as a bonus, which may vary between employees of the same project also.
- Referral bonus: Many organizations prefer to recruit staff through employee referrals. A referral drive is conducted every time there arises a vacancy. Employees are paid a bonus for every person they refer. Recruiting through referrals saves a lot of the organization’s money and effort. The company gives back to the staff in the form of bonuses.
9 non-monetary incentives
Rewards other than in the form of money are non-monetary incentives.
- Paid vacations: Employees are given days off to enjoy a vacation but are still paid for those days. A fixed number of days every year are given as paid vacations so that the employees can relax and get back to work with motivation.
- Company outings: Companies arrange yearly outings for employees and their families. This means a lot to the employees and boosts their morale. This also helps establish better relations with the staff.
- Gift cards: Some companies give away gift cards for a specific sum so that the employees can use them for shopping. Instead of buying something that is the company’s choice, they prefer to leave the choice to the sales reps.
- Membership cards: Some companies gift their staff membership cards of gyms or health clubs. This indicates their interest in the well-being of the employees. For employees who often find themselves staying late, integrating rewards such as membership cards for pre-made single meal kits can offer a much-appreciated convenience that extends beyond the usual monetary incentives.
- Work-from-home days: This is a unique incentive that plays a great role in boosting the morale of the staff. Employees can pick certain days to work from their homes. This flexibility on the part of the company helps improve the productivity of the staff.
- Trophies: Deserving employees are presented with trophies for their contribution to the company’s growth. This motivates them to give more to the company. Annual events are conducted where trophies are distributed to the best performers of every team.
- Meal coupons: Companies give coupons that can be used instead of cash at restaurants. Employees attach more value to such perks rather than monetary payment.
- Entertainment coupons: Coupons that can be used instead of cash in theatres, malls, and other entertainment zones are also given by companies.
- Training programs: Training sessions that add value to an employee’s experience are thoughtful incentives. They help in career advancement and are welcomed by employees.
Selective employees who show exemplary performance improvements can be offered such incentives. This will motivate the other team members also to put in more effort to be eligible for such training sessions.
A large CNC machine manufacturer in Asia was growing fast. They increased automation on their machines. The company had over 32 sales and service locations worldwide. They needed a strong platform to automate commissions. They wanted to give sales representatives access to incentive data. They also wanted to reduce the time it took to calculate incentives. A key goal was to lessen the need for sales managers to handle commissions manually.
Solution:
The company used Compass' sales commission management solution. Compass streamlined the commission process. It used a commission calculation and automation engine. This gave transparency. It also used a gamification platform to make selling fun. Performance was visible. Compass increased the accuracy of incentive calculations. It reduced the time to process sales commissions. This was achieved through features like program workflows and a rule engine1. Approvals, leaderboards, scorecards, and a mobile app were also used1. The mobile app allowed individuals to view their performance in real time.
Results:
The company gained real-time visibility into incentive calculations using Compass. They could also monitor payout accuracy. The sales team was engaged with quizzes, badges, and points, which improved incentive program adoption. The company also automated the commission process end-to-end. This removed the need for sales leaders to handle it manually.
Impact:
- The company saw a 20% increase in quota attainment in less than 90 days.
- Incentive program qualifiers increased by 22%.
- Platform adoption increased by 73%.
How Is incentive pay calculated?
Incentive pay varies. It depends on the company and role. Common methods exist. Some base it on individual performance. Others use team goals. Company profits can also factor in. The calculation is usually formula-based. This ensures transparency. Employees know how to earn more.
Incentive Pay = (Individual Performance / Target Performance) * Incentive Amount
How to create an incentive pay program?
Every organization follows steps to create an incentive program for its employees. The following steps can help you create an incentive program.
1. Planning
Every successful implementation starts with a plan. An organization’s incentive program also needs proper planning to identify the types of incentives, the time for payment, and the criteria for choosing an employee. Planning helps the organization fix the budget for the same.
The plan should also be communicated to the sales team to enable them to contribute effectively. The role played by the individual members and the position in the team also play a role in deciding the type of incentive. Incentive planning should be flexible since several changes may arise in the business environment.
How can Compass help?
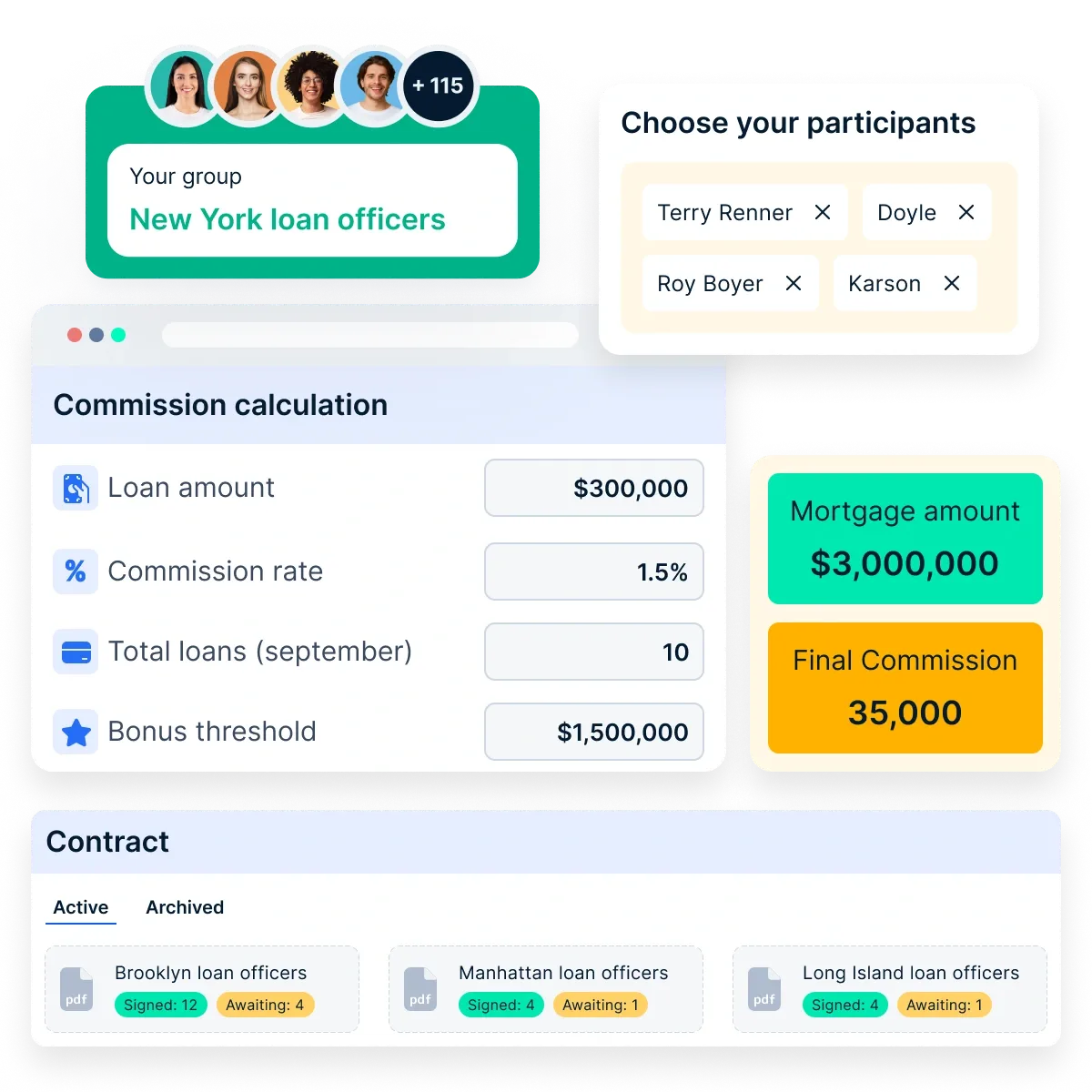
Compass helps businesses plan incentives with ease. It allows them to model different compensation plans and see their impact before finalizing. Companies can test various scenarios to find the best fit for their teams.
They can also analyze past plans to see which worked best and use them as a template. If market trends or company goals change, Compass makes it simple to adjust incentive plans anytime.
2. Monitoring
Constant monitoring is essential to keep the program up and running. Monitoring the plan helps leaders compare it with performance. The organization should identify if the sales team understands the plan. They should watch their performance to help them meet the requisite incentive criteria.
Monitoring brings to notice any lapses in the plan so that you can correct them instantly. Successful plan implementation needs the support of all team members, and monitoring helps achieve this.
How can Compass help with monitoring the plan?
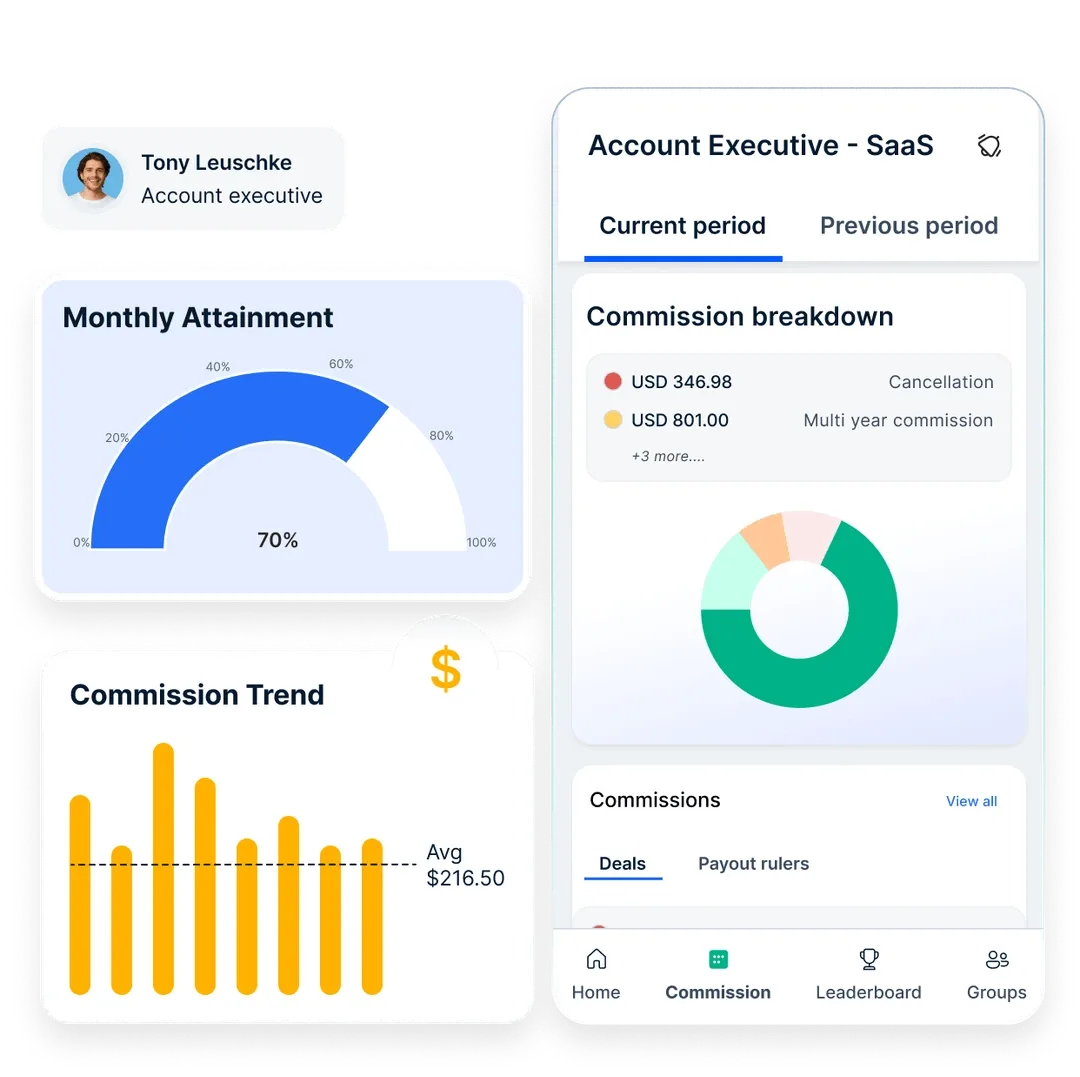
Compass helps with monitoring by providing detailed reports on quota attainment, territory performance, and plan effectiveness. It tracks sales reps' progress on a mobile app, giving managers, directors, and RevOps teams a clear view of performance.
Finance teams can analyze the revenue impact of commissions with custom reports for better budget planning. With these insights, leaders can quickly identify gaps, make corrections, and ensure the incentive plan stays effective.
3. Evaluation
Evaluation is also a part of creating an incentive program. Some organizations have mid-yearly reviews and give out incentives. Evaluation can be done after this period to determine if the program is ideal.
It helps analyze the team’s performance in relation to the plan.
Some of the questions you should ask at this step are:
- Was the program feasible?
- Did it allow enough freedom for the employees to work on the goals?
If the evaluation results indicate that the incentive program is going on smoothly, the same can be continued. If not, changes should be made to make the incentive program suitable for the employees and the business.
How can Compass help with evaluation?
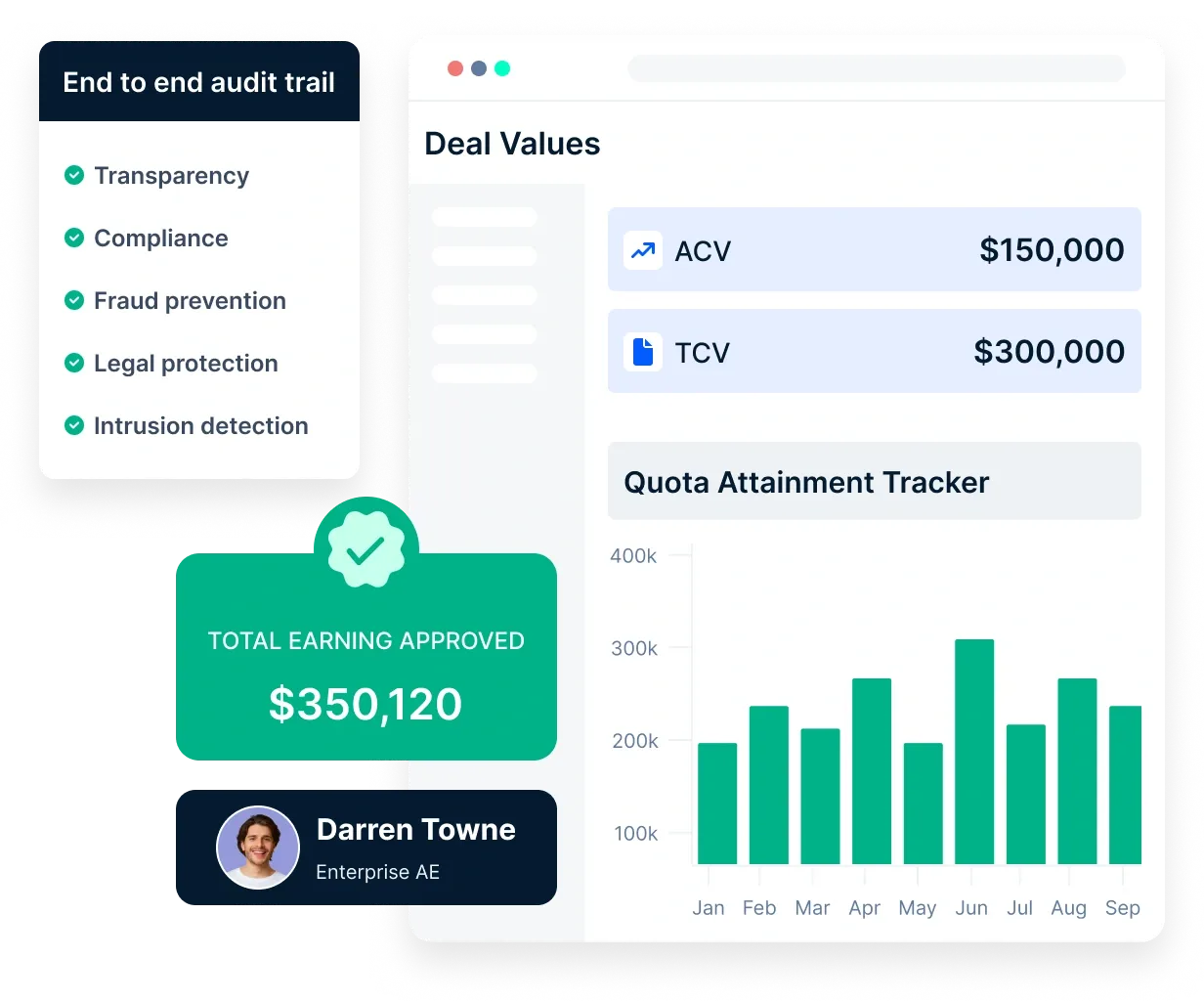
Compass helps organizations evaluate their incentive programs by providing advanced reporting, commission expense tracking, predictive analytics, and audit trails. With YTD commission reports and territory insights, businesses gain visibility into how commissions contribute to revenue.
Accurate financial reporting ensures better planning and analysis, while predictive analytics enable finance teams to assess the revenue impact of commissions for future budget allocations.
Additionally, the audit trail feature generates detailed reports on changes to sales commission plans, adjustments, and payment history, ensuring transparency and compliance. These insights help organizations determine the effectiveness of their incentive programs and make necessary adjustments for better alignment with business goals.
4. Optimization
The evaluation stage helps identify the best program for the organization. Incentives are not a one-time payout. It is a continuous process and may require revisions frequently.
Benchmarks for performance may become obsolete depending on circumstances. The company should arrive at an optimum plan program so as to be a rewarding offer to the employees.
Your business should identify and plug the gaps in the system if any. Optimizing the incentive program help in this process.
It is also important to learn how to create a good pay program. The below-mentioned tips can help!
Wrapping up
Incentive pay is a stimulant and motivates the sales team to contribute effectively. It is one of the best ways to get the employees closer to business goals. An incentive program should incorporate the above-mentioned points to be effective.
A good incentive program is beneficial for the organization as well as the employees. If you haven’t planned yours yet, remember the above points to implement a well-structured plan.
FAQs
1. Is incentive pay hourly?
No, incentive pay is generally not hourly. It's usually tied to specific performance goals.
2. What is incentive pay?
Incentive pay is compensation designed to motivate employees to achieve specific goals and improve performance.
3. Is incentive pay a raise?
No, incentive pay is not a raise. A raise is an increase to base salary. Incentive pay is variable and depends on performance.
4. What do you mean by incentive wages?
Incentive wages are earnings based on exceeding a set standard of production or sales, motivating employees to be more productive.
5. Is incentive pay worth it?
Yes, incentive pay can be worth it. Studies show optimized incentive plans can significantly boost sales and improve employee motivation.
6. Why do organizations offer incentive pay?
Organizations offer incentive pay to drive revenue growth, motivate salespeople, align employee behavior with company goals, and improve overall performance.
What is considered incentive pay? Incentive pay includes bonuses, commissions, profit sharing, performance-based pay, and other rewards tied to achieving specific targets.
Are companies required to offer incentive pay? No, companies are generally not required to offer incentive pay. It's usually at the discretion of the employer, though employment contracts may stipulate otherwise.