Comissão do agente de seguros: O que é e como funciona?
Saber como os agentes de seguros ganham através de comissões, bónus e renovações. Compreender as taxas de comissão dos agentes de seguros e os factores que afectam o seu rendimento.
Nesta página
Gerir as comissões dos agentes de seguros não se limita a calcular os pagamentos - trata-se de criar um sistema que mantenha os agentes motivados, garanta a exatidão e aumente as vendas de apólices. Com diferentes estruturas de comissões, taxas variáveis com base no tipo de seguro e vários canais de vendas envolvidos, a gestão eficiente das comissões pode ser complexa para as companhias de seguros.
Os líderes de vendas têm de equilibrar taxas de comissão competitivas com a rentabilidade do negócio, assegurando simultaneamente que os agentes se mantêm empenhados e incentivados a vender apólices com receitas elevadas.
Um modelo de comissões bem estruturado desempenha um papel fundamental na manutenção da lealdade e do desempenho dos agentes. Compreender como são determinadas as taxas de comissão, os factores que as influenciam e os componentes essenciais das estruturas de comissão ajuda as empresas a conceber um sistema de pagamento eficiente e transparente.
Quer se trate de seguros de vida, saúde ou patrimoniais, as estruturas de comissões variam, afectando a forma como os agentes abordam as vendas.
Este guia explica como funcionam as taxas de comissão de seguros, os principais elementos que moldam as estruturas de comissão e como as empresas podem otimizar os seus modelos de pagamento.
Além disso, iremos explorar a forma como as soluções modernas de gestão de comissões podem simplificar o processo, reduzir os erros e melhorar a transparência, ajudando os responsáveis de vendas e os agentes a trabalhar de forma mais eficiente.
Tipo | Primeira vez | Sobre a renovação |
Seguro de saúde | 5% a 10% | 1% a 2% |
Seguro de vida | 40% a 120% | 1% a 2% |
Seguro de habitação | 5% a 15% | 2% a 5% |
Estes aspectos podem parecer simples, mas a compreensão dos factores e conceitos subjacentes a estas comissões permite uma visão completa da comissão do agente de seguros.
Quer seja um chefe de vendas que procura otimizar os pagamentos ou um agente que procura clareza nos ganhos, este guia ajudá-lo-á a navegar eficazmente nas comissões de seguros.
Abaixo, analisamos as estruturas de comissões, as taxas e os principais factores que afectam os ganhos dos agentes, para que possa conceber um sistema de comissões competitivo e rentável.
Como funcionam as taxas de comissão de seguros e as estruturas de comissões?
As taxas de comissão de seguro variam consoante a companhia de seguros e o tipo de apólice. Vejamos como funcionam geralmente as comissões de seguros.
Uma vez que o rendimento de um agente de seguros se baseia principalmente em comissões, é fundamental estabelecer um objetivo de rendimento anual. Com base no exemplo anterior, uma venda consistente poderia gerar mais de $48.000 em comissões durante o primeiro ano. Muitos recrutadores consideram que este é um objetivo razoável. Os agentes que pretendem obter rendimentos mais elevados podem simplesmente aumentar os seus esforços de vendas para atingir os seus objectivos.
Algumas transportadoras oferecem bónus aos novos agentes para apoiar os seus rendimentos e incentivar um bom desempenho, reconhecendo que o primeiro ano pode ser difícil.
Uma das principais vantagens que algumas seguradoras oferecem é o pagamento imediato de comissões aquando da emissão da apólice. Isto significa que recebe uma parte das suas comissões de seguros assim que a cobertura começa, em vez de esperar que o titular da apólice efectue os pagamentos. Isso pode melhorar significativamente o fluxo de caixa para novos agentes de seguros.
Taxas de comissão dos agentes de seguros em função do tipo de seguro nos EUA
As taxas de comissão dos agentes de seguros nos EUApodem variar muito, dependendo do tipo de seguro, da companhia de seguros, da experiência do agente e das apólices específicas vendidas. Aqui estão algumas diretrizes gerais para tipos comuns de seguros:
Tipo de seguro | Estrutura da Comissão | Exemplo |
Seguro de vida | 40%-100% do prémio do primeiro ano, renovações mais baixas | Apólice de $5.000, 70% de comissão = $3.500 |
Seguro de saúde (mercado individual) | Média anual de $170,76 por membro | Varia consoante o segmento de mercado e a região |
Seguros de bens e acidentes | 10%-20% do prémio para novas apólices, menos renovações | Apólice de automóvel de $1.000: O agente cativo começa com $100, o agente independente ganha $150 por ano |
Seguros comerciais | 10%-15% ou mais do prémio | Com base na complexidade e dimensão da política |
Anuidades e investimentos | 1%-7% do montante investido | Varia consoante o produto e as condições |
Seguro Medicare/Cuidados a Longo Prazo | 15%-25% ou mais do prémio | Medicare Advantage: $600-$700 por plano, renovações $300-$400. Medicare Parte D: Até $100, renovações mais baixas. |
Agentes de seguros motivados e incentivados têm um melhor desempenho. Proteja-se contra a baixa produtividade de vendas com o Xododay Compass. Umaplataforma de comissões automatizadaspode agora gerir e acompanhar facilmente os programas de comissões e os KPIs da equipa.Fale com o nosso especialista em comissões.
5 Componentes das estruturas das comissões de seguros
Eis alguns componentes que pode precisar de conhecer:
1. Comissão de base
A comissão básica que um agente recebe de uma companhia de seguros quando uma apólice é vendida com sucesso é a comissão de base. É a principal fonte de rendimento que um agente recebe, independentemente da forma como fecha negócios; um vendedor recebe sempre este montante fixo de dinheiro.
2. Comissões de renovação
Se um cliente renovar o seu contrato, o vendedor recebe uma comissão de renovação. Esta comissão contínua promove um serviço consistente e incentiva os agentes a manterem ligações duradouras com os clientes.
3. Prémios baseados no desempenho
Incentivos extra dados aos agentes em resposta ao cumprimento de objectivos pré-determinados, padrões de desempenho ou metas de vendas. Estes incentivos encorajam os agentes a ter um desempenho acima e para além das expectativas.
4. Prémios de retenção
Os bónus atribuídos aos agentes por reterem os clientes e assegurarem que os segurados mantêm o seu seguro durante longos períodos são bónus de retenção. Este facto motiva os agentes a concentrarem-se na manutenção e satisfação da sua clientela.
5. Comissões suplementares
Os agentes que cumprem determinados requisitos impostos pela companhia de seguros e que vendem produtos de seguros especializados podem beneficiar desta remuneração adicional. Estas comissões adicionais funcionam como um incentivo adicional para a venda de determinados tipos de apólices.
Acelerar as vendas de apólices com a automatização das comissões
Agentes de seguros motivados e incentivados têm um melhor desempenho. Proteja-se contra a baixa produtividade de vendas com o Xododay Compass. Umaplataforma de comissões automatizadapode agora gerir e acompanhar facilmente os programas de comissões e os KPIs da equipa. Quer saber como?Fale com o nosso especialista em comissões.
Que factores influenciam o salário dos agentes de seguros?
As estruturas de comissões desempenham um papel importante na forma como os agentes de seguros ganham, mas outros factores também influenciam o seu rendimento. Estes incluem:
1. Tipo de agente
Existem dois tipos de agentes de seguros:
- Os agentes cativos vendem apólices para um único fornecedor de seguros.
- Os agentes independentes trabalham com várias companhias de seguros.
Os agentes independentes recebem normalmente comissões mais elevadas, mas também cobrem as suas próprias despesas comerciais, como a renda, o material de escritório e o marketing.
2. Tipo de apólice
Os agentes de seguros podem especializar-se num ou em vários tipos de apólices. Por exemplo, um agente de seguros de habitação pode também vender seguros de automóveis. Os agentes de seguros de vida podem expandir-se para os seguros de saúde. Para o fazer, devem cumprir os requisitos de licenciamento da sua jurisdição.
3. Localização
O local onde um agente opera afecta o seu potencial de ganhos. Uma grande cidade com uma população elevada oferece mais oportunidades de venda do que uma pequena cidade. Outros factores baseados na localização incluem:
- Acesso aos serviços públicos
- Custo de vida
- Taxas de emprego
- Segurança pública e taxas de acidentes
Estes elementos determinam a procura no mercado e influenciam a remuneração dos agentes de seguros.
Quanto ganham os agentes de seguros?
Os salários dos agentes de seguros variam. O Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reporta um salário médio anual de $79.650, ou $37 por hora. As posições de nível de entrada normalmente pagam menos. Os agentes experientes com uma forte base de clientes podem atingir rendimentos de seis dígitos. Estes dados incluem vários tipos de seguros. Estes englobam propriedade e acidentes, vida e saúde, entre outros. O BLS estima 455.540 empregos de agente de seguros.
A tabela seguinte apresenta os percentis salariais pormenorizados para os agentes de seguros. Esta tabela baseia-se nas últimas Estatísticas de Emprego e Salários do BLS (OEWS). Oferece uma perspetiva dos ganhos potenciais a diferentes níveis.
Percentil | Salário anual |
10ª | $38,210 |
25º aniversário | $51,200 |
50º (Mediana) | $65,580 |
75º aniversário | $99,840 |
90º aniversário | $128,660 |
Desafios comuns enfrentados pelos diretores de vendas na gestão das comissões dos agentes de seguros - e como Compass os resolve
Os líderes de vendas no sector dos seguros enfrentam vários obstáculos na gestão das comissões dos agentes. Com vários tipos de apólices, estruturas de pagamento complexas e uma mistura de agentes diretos, corretores e agências independentes, garantir a exatidão e a motivação torna-se uma tarefa difícil.
Erros nos pagamentos de comissões, disputas sobre deduções e falta de ferramentas de envolvimento podem levar a uma alta rotatividade de agentes e à perda de oportunidades de receita. Compass simplifica a gestão de comissões, automatizando os pagamentos, melhorando a transparência e introduzindo a gamificação para aumentar o desempenho das vendas.
Compass aborda aqui os principais desafios:
1. Imprecisão dos dados e litígios de pagamento
O acompanhamento manual das comissões através de folhas de cálculo resulta frequentemente em erros de cálculo, pagamentos incorrectos e atribuição inconsistente em diferentes canais de vendas. Os agentes que recebem comissões incorrectas podem perder a confiança no sistema, o que leva a um aumento dos litígios e a uma diminuição da motivação. A resolução destes litígios pode consumir muito tempo aos responsáveis de vendas, desviando a atenção das actividades de vendas essenciais.
SoluçãoCompass : Compass elimina a necessidade de folhas de cálculo ao centralizar o acompanhamento das comissões num único painel de controlo. Os cálculos automatizados garantem que todas as vendas de apólices são atribuídas com exatidão, reduzindo os erros de pagamento. Os agentes recebem actualizações em tempo real sobre os seus ganhos, reduzindo as disputas e promovendo a confiança na estrutura de comissões.
2. Gerir as recuperações e os estornos
Um dos aspectos mais difíceis da gestão de comissões é a recuperação de comissões pagas por apólices que são canceladas ou que são consideradas incorrectas. O tratamento manual destas questões pode ser ineficiente e suscetível de erros, conduzindo a pagamentos excessivos ou a relações tensas com os agentes. Políticas de reembolso pouco claras podem causar litígios e desencorajar os agentes de venderem apólices de elevado valor.
SoluçãoCompass : Compass automatiza as provisões de reembolso, garantindo que as deduções por apólices canceladas, violações de contrato ou declarações falsas sejam processadas sem problemas. O sistema fornece documentação clara e em tempo real dos cálculos de reembolso, garantindo que os agentes compreendam as deduções e minimizando os conflitos.
3. Falta de visibilidade das estruturas das comissões
Uma frustração comum entre os agentes de seguros é a falta de clareza na forma como as suas comissões são calculadas. Sem visibilidade das estruturas de comissões, os agentes podem sentir-se desmotivados ou cépticos em relação aos seus pagamentos. Os chefes de vendas têm muitas vezes dificuldade em comunicar eficazmente as actualizações ou alterações das estruturas de comissões, o que leva a mal-entendidos e ao desinteresse.
SoluçãoCompass : Compass fornece um sistema de gestão de comissões transparente, onde os agentes podem aceder a análises em tempo real dos seus ganhos. Através de um painel de controlo de fácil utilização, os agentes podem acompanhar o seu desempenho, ver os cálculos de pagamento e transferir documentos da estrutura de incentivos. Este nível de transparência ajuda os agentes a manterem-se motivados e reduz os pedidos de informação sobre os ganhos.
4. Motivar os agentes a venderem apólices com receitas elevadas
Muitos agentes de seguros concentram-se em apólices fáceis de vender e de baixo valor, que podem não contribuir significativamente para a receita da empresa. Sem incentivos claros orientados para a receita, os agentes podem não ter a motivação para dar prioridade às apólices que geram maiores lucros para a empresa. Isto resulta num desempenho de vendas abaixo do ideal e na perda de oportunidades de crescimento.
SoluçãoCompass : Compass permite que os diretores de vendas implementem KPIs estruturados orientados para as receitas que alinham as comissões com as apólices de receitas elevadas. Ao oferecer incentivos mais elevados para as apólices que geram mais valor comercial, Compass garante que os agentes são motivados a dar prioridade a estas vendas. O sistema automatizado actualiza dinamicamente as projecções de ganhos, mostrando aos agentes os benefícios financeiros diretos da venda de apólices mais lucrativas.
5. Manter os agentes envolvidos e reduzir a rotatividade
Sem um envolvimento contínuo, os agentes podem perder o interesse ou procurar oportunidades junto de concorrentes que ofereçam incentivos mais atractivos. As estruturas tradicionais de comissões carecem frequentemente de elementos interactivos que mantenham os agentes motivados. Os diretores de vendas têm dificuldade em manter níveis elevados de envolvimento, o que leva a uma menor produtividade e a uma maior rotatividade.
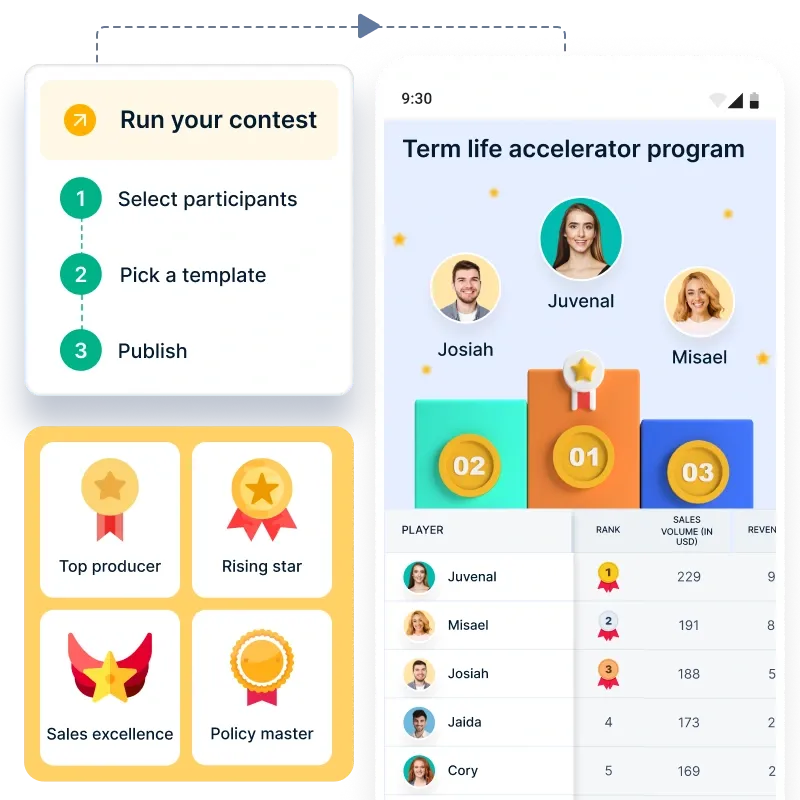
SoluçãoCompass : Compass introduz a gamificação no processo de vendas, transformando a venda baseada em comissões numa experiência dinâmica e envolvente. Os concursos de vendas, as tabelas de classificação em tempo real e os cartões de pontuação de desempenho incentivam os agentes a ultrapassar os seus limites. As empresas podem criar concursos personalizados em diferentes tipos de apólices, recompensando os melhores desempenhos com bónus, reconhecimento e oportunidades de crescimento na carreira. Esta abordagem não só aumenta o desempenho das vendas, como também reforça a lealdade dos agentes.
Em suma
O conhecimento da economia das comissões dos agentes de seguros realça a ligação crucial entre os sistemas de incentivos que regulam a sua remuneração e a forma como motivam os agentes.
Uma vez que o pagamento de comissões é o fator de motivação dos agentes, torna-se fundamental que as companhias de seguros tratem eficazmente a remuneração dos seus agentes.
É aqui que o software de compensação de vendas -Compasssurge como uma ferramenta vital.
Uma solução abrangente que simplifica e gere as complexidades das estruturas de comissões.
Permite às seguradoras:
- calcular efetivamente,
- pista, e
- pagar as comissões aos seus agentes
Se quiser saber mais, como é que Compass pode automatizar o pagamento das comissões do seu agente de seguros, entãoreserve a demonstraçãoagora!
FAQs
1. Quais são as comissões dos agentes de seguros?
As comissões dos agentes de seguros variam consoante o tipo de apólice, a seguradora e a região. Normalmente, as comissões de seguros de vida variam entre 30% e 90% do prémio do primeiro ano, enquanto as comissões de seguros de saúde e de propriedade rondam os 5% a 20% por apólice.
2. Qual é a melhor comissão para um agente de seguros?
A melhor comissão depende do tipo de apólice. Os seguros de vida oferecem as comissões mais elevadas (até 90% no primeiro ano), mas as comissões de renovação baixam significativamente. Os seguros de bens e acidentes oferecem comissões iniciais mais baixas, mas oferecem renovações estáveis.
3. Os vendedores de seguros ganham bem?
Sim, os agentes de seguros bem sucedidos podem ganhar bem, especialmente aqueles que vendem apólices com comissões elevadas (por exemplo, seguro de vida) e retêm clientes para comissões de renovação. O rendimento varia consoante a experiência, as competências de venda e a seguradora.
4. Qual é um bom rácio de comissão em seguros?
Um bom rácio de comissões equilibra as comissões iniciais e de renovação. Um rácio saudável é de 40-70% para o primeiro ano de seguro de vida e 10-15% para as renovações, enquanto as comissões de seguro de imóveis variam normalmente entre 10-20% e as renovações entre 5-10%.