Clawback em vendas e comissões: Significado, exemplos, parâmetros de referência
O reembolso nas vendas ajuda as empresas a recuperar as comissões de negócios falhados, a reduzir os riscos financeiros e a incentivar práticas de vendas éticas. Saiba como funciona e porque é que é essencial para um crescimento sustentável das vendas.
Nesta página
O que começou por ser uma forma de evitar comportamentos imprudentes das empresas e de proteger os interesses dos acionistas devido ao escândalo de vendas cruzadas do Well Fargoescândalo de vendas cruzadas do Wells Fargoo clawback tornou-se rapidamente uma prática adoptada por várias empresas em todo o mundo. Além disso, colocou a necessidade de fundamentar aLei Dodd-Frankna política.
O incidente ocorreu em 2016, o que levou o Wells Fargo a rever os seus quadros de gestão, risco e controlo. O Wells Fargo também alterou a sua cultura e as suas políticas de recuperação de créditos para restabelecer a confiança e resolver os problemas que estiveram na origem do escândalo. No entanto, o incidente abriu uma oportunidade para as empresas de diferentes sectores a nível mundial reverem as suas políticas de clawback.
A política de clawback é vista como uma ferramenta nas organizações para desencorajar a assunção de riscos excessivos e inadequados por parte dos representantes. Em 2016,funcionários do Wells Fargo5.300, para ser exato, abriram 2 milhões de contas não autorizadas, o que levou o banco a recuperar 185 milhões de dólares em compensação executiva. Este facto vem restabelecer o objetivo da política de reembolso.
O objetivo era permitir que uma empresa recuperasse a compensação baseada em incentivos paga a um executivo, se mais tarde se viesse a verificar que as demonstrações financeiras que continham esses indicadores eram incorrectas ou não tinham origem ética. Tomando o Wells Fargo como exemplo contemporâneo de "clawing back", pode dizer-se que as consequências da violação de uma política de clawback podem ser significativas.
O que é o clawback?
Clawback, de acordo comNASDAQrefere-se a "um acordo pelo qual os proprietários de acções se comprometem a utilizar os dividendos que receberam no passado para financiar as necessidades de tesouraria do projeto ou da empresa no futuro".
Em termos simples, o clawback é uma disposição contratual que permite a uma empresa retirar compensações ou benefícios previamente pagos, normalmente associados a remunerações baseadas no desempenho, como bónus.
O seu objetivo é garantir a responsabilização dos trabalhadores. Permite que a organização recupere a compensação se um funcionário se envolver em má conduta ou se houver uma correção significativa dos registos financeiros.
Agora que já compreendemos o significado de clawback, vamos analisar como funciona o mecanismo da provisão de clawback.
O que é a cláusula de clawback e como funciona?
As cláusulas de reembolso referem-se a cláusulas contratuais que exigem a devolução de dinheiro ou outra compensação em circunstâncias ou eventos específicos. São frequentemente utilizadas em contratos de trabalho financeiros para regular o pagamento de bónus e proteger contra perdas financeiras, fraude ou má conduta. As cláusulas de reembolso são concebidas de forma a promover melhores práticas financeiras, impedir actividades fraudulentas e incentivar um comportamento de vendas sustentável.
No sector financeiro, os clawbacks são normalmente aplicados aos contratos de trabalho para controlar a remuneração dos executivos e evitar a fraude. Podem ser acionados por variações a longo prazo dos instrumentos financeiros, má conduta ou relatórios financeiros incorrectos. A lei Dodd-Frank tinha como objetivo alargar ainda mais as restituições, mas a regra proposta não foi aprovada.
Para organizações de vendas,cláusulas de clawbackpermitem que uma empresa recupere a comissão ou outra compensação baseada no desempenho paga a um vendedor quando um cliente desiste ou cancela a compra num determinado período.
Este facto ajuda a proteger a empresa de perdas financeiras devidas à rotatividade dos clientes e incentiva os representantes de vendas a procurarem negócios de alta qualidade e a melhorarem a experiência do cliente.
- Entre 2005 e 2010, o número de grandes empresas da Fortune 500 que utilizam clawbacks aumentou muito. No início, menos de 3% utilizavam-no, mas depois saltou para82%.
- De acordo com a ISS Corporate Solutions, mais de90%das empresas do S&P 500 têm regras para recuperar dinheiro e acções. Mas para o Russell 3000, que não inclui o S&P 500, apenas um pouco mais de metade tem políticas semelhantes.
- Umestudo realizado em Harvardrevelou uma taxa de adoção de 94% entre as empresas de cuidados de saúde do S&P 500. No entanto, apenas cerca de 31% das empresas do sector da saúde fora do S&P 500 têm políticas deste tipo em vigor.
O estudo quantificado das sementes do clawback mostra a importância de incluir a política de clawback no acordo. No entanto, há mais razões para incluir a política de reembolso nos planos de comissões de vendas.
No entanto, para incluir a política de clawback na sua disposição, é necessário conhecer os tipos de clawback existentes.
Tipos de cláusulas de clawback
Eis os tipos de cláusulas de clawback com breves explicações e exemplos:
1. Crédito de quota negativo
Este tipo de clawback reduz a comissão ou o bónus de um empregado se este não atingir um objetivo de vendas específico. Digamos que um vendedor ganha um bónus de 5.000 dólares por exceder a sua quota em 10%.
Mas, se a cláusula incluir um crédito de quota negativo e o vendedor não atingir a sua quota em 5%, uma parte do seu salário base ou comissões anteriores pode ser reduzida num montante proporcional à quota não atingida.
2. Crédito retroativo de quotas negativo
Semelhante a um crédito de quota negativo, esta disposição permite que o empregador recupere comissões ou bónus já pagos ao trabalhador se este não cumprir a sua quota dentro de um determinado prazo, que pode ir além do período de vendas em curso.
3. Reembolso apenas da comissão
Este clawback aplica-se apenas às comissões ganhas pelo empregado. Se o colaborador não cumprir determinados parâmetros de desempenho ou violar o seu contrato, a empresa pode reter ou recuperar a totalidade ou uma parte das comissões pagas.
Exemplos de cláusulas de reembolso em comissões de vendas
Os reembolsos nas vendas são essenciais para manter uma estrutura de comissões justa e, ao mesmo tempo, proteger as empresas de riscos financeiros. Abaixo, exploramos três métodos comuns para lidar com cenários de reembolso de vendas.
Quotas e estrutura de comissões
Digamos que a Ema ganha uma comissão com base na receita recorrente anual (ARR) de negócios fechados num período de quota. Nos períodos 1 e 2, as quotas são de $150.000 e $300.000, respetivamente. A Ema recebe uma comissão de 10% sobre a ARR do negócio até atingir a sua quota (Nível 1) e 20% por qualquer montante que exceda a quota (Nível 2).
Comissão e regras de reembolso
As comissões são pagas sobre as reservas, mas estão sujeitas a uma cláusula de reembolso em caso de não pagamento por parte do cliente. Abaixo estão os negócios fechados para os Períodos 1 e 2. No final do Período 2, a empresa determina que o Negócio A não vai pagar, accionando um clawback de vendas.
Método de reembolso #1: montante exato do pagamento
Este é o método mais comum devido à sua simplicidade operacional e natureza intuitiva para as equipas de vendas.
Uma vez que a Ema ganhou uma comissão de $5.000 pelo negócio A, que não foi concretizado, tem de devolver $5.000.
Este método associa os montantes de clawback ao momento em que um negócio foi fechado dentro do período de quota. Por exemplo, como o negócio A foi fechado no nível 1, o montante do clawback é 10% da ARR. No entanto, se o negócio C tivesse sido objeto de clawback, o montante teria sido de $15.000 (20% da ARR).
Porque é que gostamos do Método #1
- Muito intuitivo e fácil de compreender.
- Simples tanto para os empregadores como para os vendedores.
- Assegura a equidade nas recuperações de comissões de vendas.
Método de reembolso #2: crédito de quota negativo para o período atual
Este método reduz o crédito de quota do Período 2 ao tratar o clawback como um montante de venda negativo, reduzindo efetivamente a realização do período atual.
Ao adicionar o clawback do negócio A como uma venda negativa, este método é fácil de automatizar em folhas de cálculo e CRMs. No entanto, pode incentivar os representantes de vendas a adiar negócios para períodos futuros para evitar impactos negativos nas quotas.
Porque gostamos do Método #2
- Operacionalmente simples e fácil de automatizar.
- Declarações de comissão claras.
- Elimina a necessidade de referência histórica de pagamentos.
Método de reembolso #3: crédito de quota negativo para o período anterior
Este método ajusta retroativamente a realização da quota do período anterior para refletir o clawback. Ao contrário do método n.º 2, este método evita incentivos negativos no período atual.
Este método é mais complexo, uma vez que requer o recálculo de comissões passadas e o ajustamento dos pagamentos em conformidade. As empresas que utilizam a ASC 606 para a capitalização de custos têm de garantir a conformidade adequada ao implementar este método.
Porque gostamos do Método #3
- Equilibra a equidade entre o empregador e o vendedor.
- Evita incentivos negativos para adiar as vendas.
- Evita um impacto negativo nas comissões do período atual.
Considerações finais
As disposições de reembolso nas vendas garantem a segurança financeira das empresas, mantendo simultaneamente uma estrutura de comissões justa.
Quais são os parâmetros de referência comuns utilizados para determinar o clawback nas vendas?
Os parâmetros de referência mais comuns utilizados para determinar o clawback nas vendas são:
1. Cumprimento das quotas
Este é o parâmetro de referência mais fundamental. As cláusulas de reembolso são frequentemente aplicadas se um vendedor ficar abaixo de uma percentagem predefinida da sua quota de vendas atribuída durante um período específico.
2. Aceleradores de vendas
Trata-se de bónus ou incentivos oferecidos aos vendedores por excederem objectivos específicos. Estes aceleradores podem ser objeto de reembolso se o vendedor não atingir a quota de base subjacente ou outros indicadores de desempenho.
No entanto, as empresas devem comunicar claramente com os representantes de vendas sobre a integração das cláusulas de clawback e as suas implicações. Isto pode ajudar a evitar mal-entendidos e a garantir que os representantes de vendas compreendem as potenciais consequências das suas acções. Para tal, seria útil manter as melhores práticas de navegação com clawback.
Por que razão deve incluir cláusulas de clawback nos seus planos de comissões de vendas?
É essencial incluir cláusulas de reembolso nos planos de comissões de vendas para proteger a empresa de perdas financeiras devido a actividades fraudulentas, vendas ilegais ou incumprimento das políticas da empresa. Considere a inclusão de cláusulas de clawback nos seus planos de comissões de vendas por várias razões fundamentais:
1. Redução do risco financeiro
Os reembolsos podem ajudar a reduzir o risco financeiro, recuperando as comissões sobre as vendas que não se traduzem em benefícios a longo prazo para a empresa. Isto pode dever-se à perda de clientes, devoluções de produtos ou actividades fraudulentas.
A política aplica-se se as demonstrações financeiras da Airbnb divulgadas publicamente tiverem de ser reformuladas devido a má conduta fraudulenta ou intencional por parte dos funcionários ou executivos.
A política permite que o Comité de Desenvolvimento de Liderança, Pertença e Compensação ou o conselho de administração recuperem incentivos em dinheiro, prémios em acções ou outras compensações dos funcionários culpados.
2.Proteção jurídica reforçada
As cláusulas de reembolso proporcionam uma camada de proteção jurídica em casos de fraude ou má conduta por parte de um vendedor. Se uma comissão foi ganha através de meios ilegais ou pouco éticos, a cláusula de clawback permite à empresa recuperar esses fundos.
3. Alinhamento com os objectivos da empresa
As cláusulas de reembolso podem incentivar comportamentos de vendas que contribuam para o crescimento da empresa a longo prazo. Ao recuperar potencialmente as comissões sobre os ganhos a curto prazo que não se traduzem na retenção ou satisfação do cliente, as cláusulas de reembolso incentivam os vendedores a concentrarem-se na criação de valor sustentável.
Esta regra aplica-se a remunerações de incentivo recebidas após 2 de outubro de 2023. Um comité nomeado pelo conselho de administração supervisionará este processo e seguirá a Regra 5608 da Nasdaq.
4. Incentivar os comportamentos de venda
Os reembolsos nas vendas desempenham um papel crucial na melhoria da experiência global do cliente. Em vez de receberem a sua comissão e seguirem em frente, os representantes de vendas têm interesse em garantir a satisfação do cliente durante todo o processo de integração.
Isto é particularmente valioso para os fornecedores de SaaS e outras empresas baseadas em subscrições, onde a retenção a longo prazo supera o impacto de uma única venda. Ao implementar uma estrutura de comissões de vendas com clawback, as empresas dão aos seus representantes uma motivação extra para se alinharem com esta mentalidade de sucesso a longo prazo.
Como Compass simplifica a gestão do clawback
Compass simplifica o processo de clawback, garantindo precisão, transparência e eficiência.
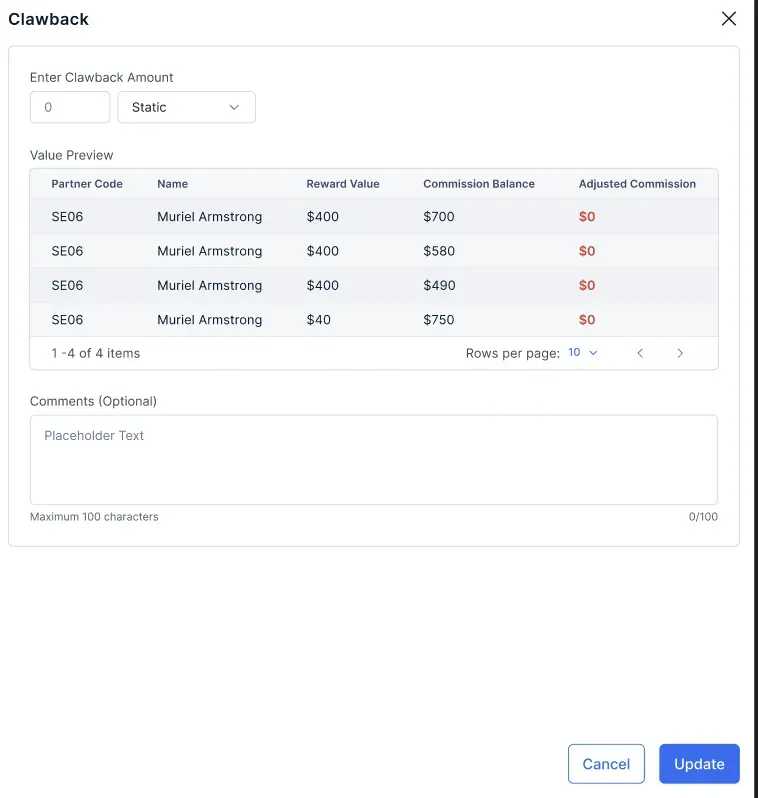
Eis como funciona:
- Identificação de transacções e participantes - Compass ajuda a identificar transacções passadas que requerem recuperação e identifica os participantes envolvidos.
- Determinação dos ajustamentos das comissões - Calcula o montante pago aos participantes e determina o montante do clawback com base numa lógica pré-definida, como uma percentagem da comissão paga.
- Processo de dedução sem falhas - O montante recuperado é ajustado a partir da comissão do mês atual ou de pagamentos futuros, garantindo uma interrupção mínima.
- Validação e aprovação - A validação de dados e os fluxos de trabalho de aprovação predefinidos garantem a exatidão antes do processamento de qualquer reembolso.
- Transparência total - Os utilizadores finais ganham visibilidade total dos seus clawbacks, incluindo detalhes sobre negócios, montantes deduzidos e quaisquer comentários relevantes dos aprovadores.
- Reembolsos ad-hoc - Os administradores têm a flexibilidade de iniciar reembolsos para pagamentos específicos de qualquer plano de comissões, com uma pista de auditoria dedicada tanto para administradores como para utilizadores.
Através do Compass, os administradores podem configurar e gerir eficazmente as disposições de reembolso, enquanto os utilizadores finais podem acompanhar convenientemente os seus reembolsos através da aplicação móvel.
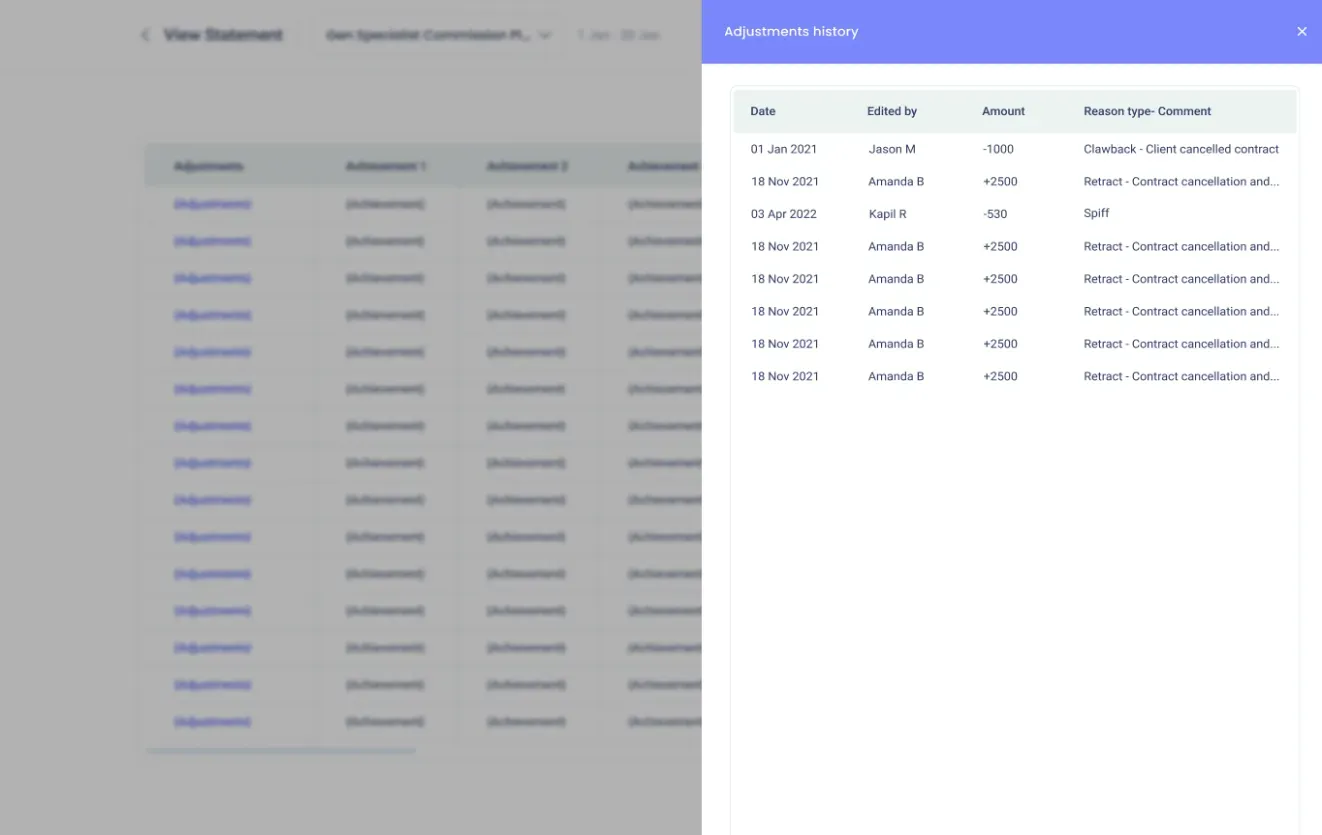
Além disso, os utilizadores podem visualizar, enviar por e-mail ou descarregar as suas transacções relevantes, assegurando um controlo total e transparência sobre os seus ajustes de comissões. Agendar uma chamada agora!
Melhores práticas para navegar nas cláusulas de clawback
Para navegar eficazmente nas cláusulas de clawback, é importante seguir várias boas práticas. Estas práticas incluem:
1. Procurar aconselhamento jurídico
É fundamental consultar peritos jurídicos aquando da criação de cláusulas de clawback para garantir que são legalmente válidas e aplicáveis. Isto pode evitar potenciais litígios e acções judiciais.
2. Estabelecer condições claras e equitativas de reembolso
As cláusulas de reembolso devem ser diretas e justas, com condições transparentes que definam quando as comissões podem ser reclamadas. Isto ajuda a evitar mal-entendidos e garante que os representantes de vendas estão conscientes das potenciais consequências das suas acções.
3. Rever e atualizar regularmente as cláusulas de clawback
As empresas devem analisá-las e revê-las periodicamente para manter a sua eficácia e relevância. Este processo pode envolver a análise de casos passados em que a cláusula foi invocada para avaliar o seu impacto no desempenho financeiro da empresa e nos resultados das vendas.
Leis recentes relativas às cláusulas de clawback
- Asnovas regrasimplementadas em outubro de 2022, fazem parte da Lei Dodd-Frank de Reforma de Wall Street e Proteção do Consumidor de 2010.
- As empresas cotadas em bolsa devem seguir as novasRegras de reembolso da SEC.
- Estas regras exigem que as empresas recuperem a compensação baseada em incentivos concedida com base em erros nas demonstrações financeiras. Isto aplica-se à maioria das empresas das principais bolsas de valores, independentemente do conhecimento ou da má conduta do funcionário.
- De acordo comleis recentesas empresas não podem proteger os seus funcionários contra estas restituições e tanto os erros contabilísticos maiores como os menores podem desencadear estas restituições.
- As novas regras de divulgação exigem que as empresas comuniquem pormenores sobre as restituições. As regras podem também afetar a forma como as empresas conduzem as investigações internas.
Conclusão
As cláusulas de reembolso desempenham um papel significativo nos enquadramentos, restabelecendo a confiança dos investidores e fomentando a confiança do público. A sua inclusão melhora a responsabilização individual e modifica os sistemas de incentivos para reduzir a dependência dos resultados dos pagamentos a curto prazo.
Pode dizer-se que os clawbacks são implementados em sectores como o das participações privadas, seguros, dividendos e contratos comerciais para garantir uma maior responsabilidade entre as partes envolvidas.
No entanto, para garantir uma aplicação justa das políticas de clawback entre os representantes de vendas, pode ser criado um canal de automatização de incentivos para que estes cumpram as expectativas definidas no contrato.Compassé um software de gestão de incentivos de vendas que ajuda as empresas a gerir e automatizar os seus programas de incentivos de vendas de forma justa. A plataforma simplifica a gestão de planos de incentivos complexos ao:
- Lançamento de planos de incentivos
- Cálculo e pagamento de incentivos, com visibilidade em tempo real do desempenho
- Gerar informações sobre comissões e pagamentos atempados.
- Integração com CRMs através de webhooks, APIs ou SDKs, incorporando filtros de ligação e de porta para gerir várias fontes de dados.
Por isso, facilite a automatização de programas de incentivos, simplifique o processo de estabelecimento de objectivos de desempenho de vendas e monitorize o progresso dos funcionários na superação dos mesmos, mantendo o decoro e a justiça a todos os níveis com o Compass.